🌱✨ DNA Data Storage: When Biology Meets the Information Age ✨🧬
Have you ever stopped to think about where all our data—every photo, message, song, and document—will eventually live? Our current hard drives and cloud servers are amazing, but they’re starting to struggle under the sheer weight of our digital lives. 📈
What if I told you that one of the most promising solutions comes not from Silicon Valley, but from nature itself? Enter DNA data storage—a mind-blowing fusion of biology and computer science that could change everything. 🧪💾
🧠 So, Why Do We Need DNA to Store Data?
We’re generating data at an absolutely insane rate. Think about every search query, every social media post, every high-resolution video. Traditional storage methods (like magnetic tapes and hard drives) are hitting their limits:
- 📈 They’re running out of space: We’re approaching the physical limit of how much data we can squeeze onto a disk.
- 🔧 They’re high-maintenance: They degrade over time, need constant energy to maintain, and require expensive cooling systems.
- ⚡ They’re energy-hungry: Data centers already consume a massive amount of the world's electricity.
Meanwhile, DNA—the molecule that nature uses to store the blueprint of life—has been doing this efficiently for billions of years. It’s the ultimate storage device:
- 🧪 Unbelievable Density: A single gram of DNA could theoretically hold over 200 petabytes of data. That’s like storing the entire content of the internet in a shoebox!
- 🌡️ Incredibly Durable: Under the right conditions, DNA can last for thousands of years. We’ve sequenced DNA from ancient mammoths!
- 🔒 Never Becomes Obsolete: The "language" of DNA (A, C, G, T) will never go out of style. We’ll always be able to read it.
- 💡 Energy Efficient: Once it’s written, it doesn’t need any power to store the information. Just keep it cool and dry.
It sounds like science fiction, but researchers are already doing it in labs around the world!
🧪 How Does It Actually Work?
The process is like a super high-tech translation service between the digital and biological worlds.
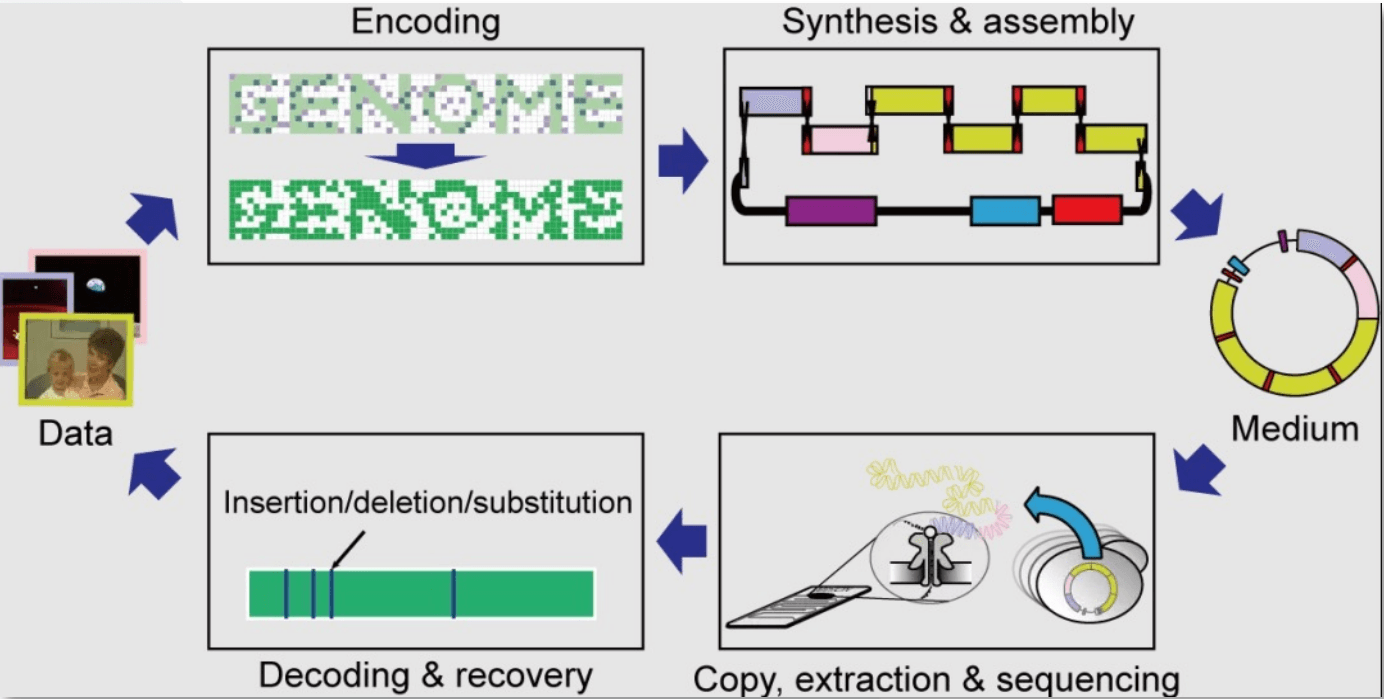
- ENCODING 🔢→🧬: Software translates the 0s and 1s of a digital file into a sequence of the four DNA "letters": A, C, G, and T.
- SYNTHESIS (Writing) ✍️: A machine uses chemical or enzymatic processes to build that specific sequence of DNA from scratch.
- STORAGE 🧊: The synthetic DNA is carefully stored, often encapsulated in a tiny glass bead or tube to protect it from moisture and damage.
- SEQUENCING (Reading) 🔍: When the data is needed, the DNA is "read" using a sequencer (like a tiny nanopore reader) that identifies the order of the letters.
- DECODING 🧬→🔢: Software reverses the process, translating the A/C/G/T sequence back into the original 0s and 1s, reconstructing your file perfectly!
It’s essentially using biology’s own information system to store our digital world. How cool is that?